ISO 50001, titled “Energy Management Systems – Requirements with guidance for use,” is an international standard developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its primary purpose is to help organizations in all sectors use energy more efficiently by establishing a comprehensive energy management system (EnMS). This standard provides a structured approach to improving energy performance, enhancing energy efficiency, security, and reducing overall energy consumption.
Key Benefits of ISO 50001
Organizations adopting ISO 50001 stand to gain numerous advantages, including:
- Energy Cost Reduction: By systematically managing energy use, organizations can identify inefficiencies and reduce unnecessary energy consumption, leading to significant cost savings.
- Improved Environmental Impact: As energy use decreases, so does the carbon footprint of the organization. This supports efforts to mitigate climate change and meet national or self-imposed carbon reduction targets.
- Enhanced Corporate Reputation: Achieving ISO 50001 certification showcases an organization’s commitment to sustainability and social responsibility, boosting its public image and increasing consumer trust.
Core Objectives of ISO 50001
The main goal of ISO 50001 is to provide organizations with a framework to:
- Identify Energy Efficiency Opportunities: Through a thorough assessment, companies can pinpoint areas where energy use can be reduced.
- Implement Continuous Improvement: The standard advocates for the continuous monitoring and improvement of energy performance over time.
- Cost Savings: With optimized energy use, organizations can reduce energy costs, thereby enhancing profitability.
Structure of ISO 50001:2018
ISO 50001 follows a structured framework similar to other ISO management systems like ISO 9001 (Quality Management Systems) and ISO 14001 (Environmental Management Systems). This makes it easier to integrate ISO 50001 with other management systems in an organization.
Here’s a breakdown of the key components in the 2018 version of ISO 50001:
- Scope: Defines the extent of the energy management system.
- Context of the Organization: Ensures that energy management aligns with the organization’s strategic objectives.
- Leadership: Outlines the role of leadership in driving energy management initiatives.
- Planning: Establishes energy management goals and objectives.
- Support: Addresses the resources, awareness, and competence required for effective implementation.
- Operation: Focuses on the implementation of energy-saving measures.
- Performance Evaluation: Ensures that energy performance is consistently reviewed and improved.
- Improvement: Emphasizes the ongoing development and optimization of the energy management system.
The PDCA Cycle: A Continuous Improvement Approach
ISO 50001 is based on the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, which encourages a continual improvement process:
The 4 phases of the PDCA circle
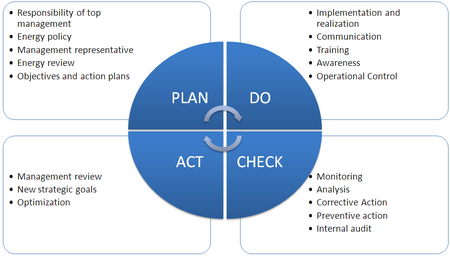
- Plan: Set clear energy management goals, identify energy performance indicators, and define action plans to meet energy targets.
- Do: Implement energy management processes, allocate resources, and assign responsibilities.
- Check: Monitor performance, conduct internal audits, and evaluate the effectiveness of the energy management system.
- Act: Based on audits and reviews, take corrective or preventive actions to ensure energy targets are consistently met and exceeded.
ISO 50001 vs. ISO 14001
While both ISO 50001 and ISO 14001 focus on improving the environmental footprint of an organization, they differ in their approach:
- ISO 50001 is specifically designed to address energy use, performance, and efficiency. It is data-driven and focuses on achieving measurable energy performance improvements.
- ISO 14001 covers a broader range of environmental impacts, including waste, emissions, and natural resource use, with a focus on overall environmental management.
For organizations where energy is a significant cost or environmental impact, ISO 50001 may offer a more focused and actionable framework compared to ISO 14001.
Why Certification Matters
Certification to ISO 50001 demonstrates that an organization has implemented an effective energy management system that meets global standards. It provides several benefits:
- Public Assurance: Certification serves as proof to customers, stakeholders, and regulatory bodies that an organization is committed to energy efficiency.
- Continual Improvement: It ensures ongoing energy performance improvements and cost reductions.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Certification helps organizations comply with local and international energy management regulations.
Impact of ISO 50001 Certification
Early adopters of ISO 50001 have already reported impressive energy savings and reductions in carbon emissions. For example:
- Delta Electronics in China reduced power consumption by 10.51 million kWh, saving $1.2 million and reducing 10.2 thousand tons of carbon emissions.
- Sheffield Hallam University in the UK reduced its carbon emissions by 11%, saving £100,000 annually after certification.
ISO 50001 certification is not just about compliance; it’s a pathway to substantial operational efficiency, cost savings, and environmental stewardship.
Conclusion
ISO 50001 provides a robust framework for organizations to systematically manage and improve energy performance. By adopting this standard, businesses can reduce energy consumption, cut costs, and improve their environmental footprint. As global energy demand increases, ISO 50001 will play a crucial role in helping organizations transition to more sustainable practices while driving operational efficiency and competitive advantage. Whether integrated with other management systems or adopted independently, ISO 50001 is an essential tool for businesses aiming to enhance their energy management practices.
